【狂神说Java】注解和反射
注解



1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| package com.zq.Annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation {
String name() default "zq";
int age();
}
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface MyAnnotation2 {
String value();
}
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@MyAnnotation(age = 18)
public void test() {
}
@MyAnnotation2("jamay")
public void test2() {
}
}
|
反射



1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| package com.zq.Reflect;
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.zq.Reflect.user");
System.out.println(c1);
Class c2 = new user().getClass();
Class c3 = user.class;
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
Class c4 = Integer.TYPE;
}
}
class user {
private String name;
private int id;
public user(String name, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
}
public user() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "user{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
}
|

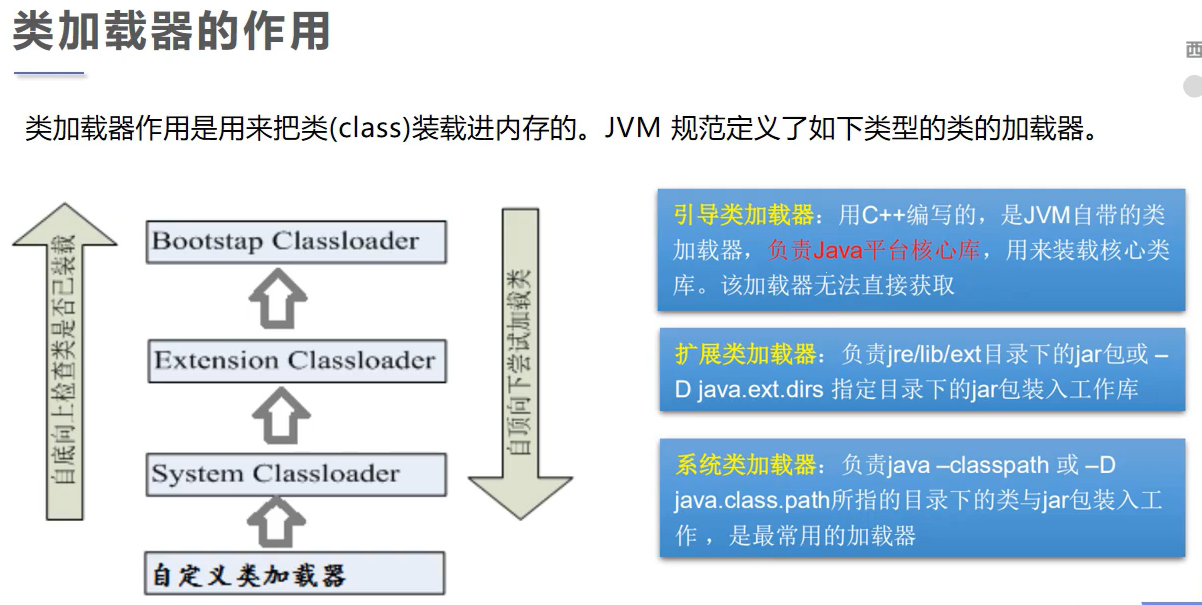
双亲委派机制
原理:
- 如果一个类加载器收到了类加载请求,它并不会自己先加载,而是把这个请求委托给父类的加载器去执行
- 如果父类加载器还存在其父类加载器,则进一步向上委托,依次递归,请求最终将到达顶层的引导类加载器;
- 如果父类加载器可以完成类加载任务,就成功返回,倘若父类加载器无法完成加载任务,子加载器才会尝试自己去加载,这就是双亲委派机制
- 父类加载器一层一层往下分配任务,如果子类加载器能加载,则加载此类,如果将加载任务分配至系统类加载器也无法加载此类,则抛出异常
作用:
- 避免类的重复加载(最开始时没有缓存, 逐步向上, 再向下, 某一层将类加载并缓存. 再次加载时, 已有缓存, 不再向上询问)
- 保护程序安全,防止核心API被随意篡改
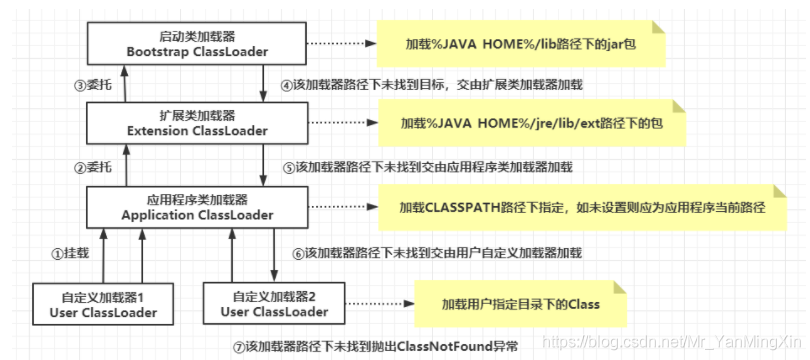
- 打破双亲委派
- 自定义类加载器,重写loadClass方法
- 使用线程上下文类加载器
有了Class对象, 能做什么

创建对象
1
2
| Class c1 = Class.forName("com.zq.Reflect.user");
user u = (user)c1.newInstance();
|
1
2
3
4
| Class c1 = Class.forName("com.zq.Reflect.user");
Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class);
user zq = (user)constructor.newInstance("zq", 18);
System.out.println(zq);
|
通过反射调用类中的方法
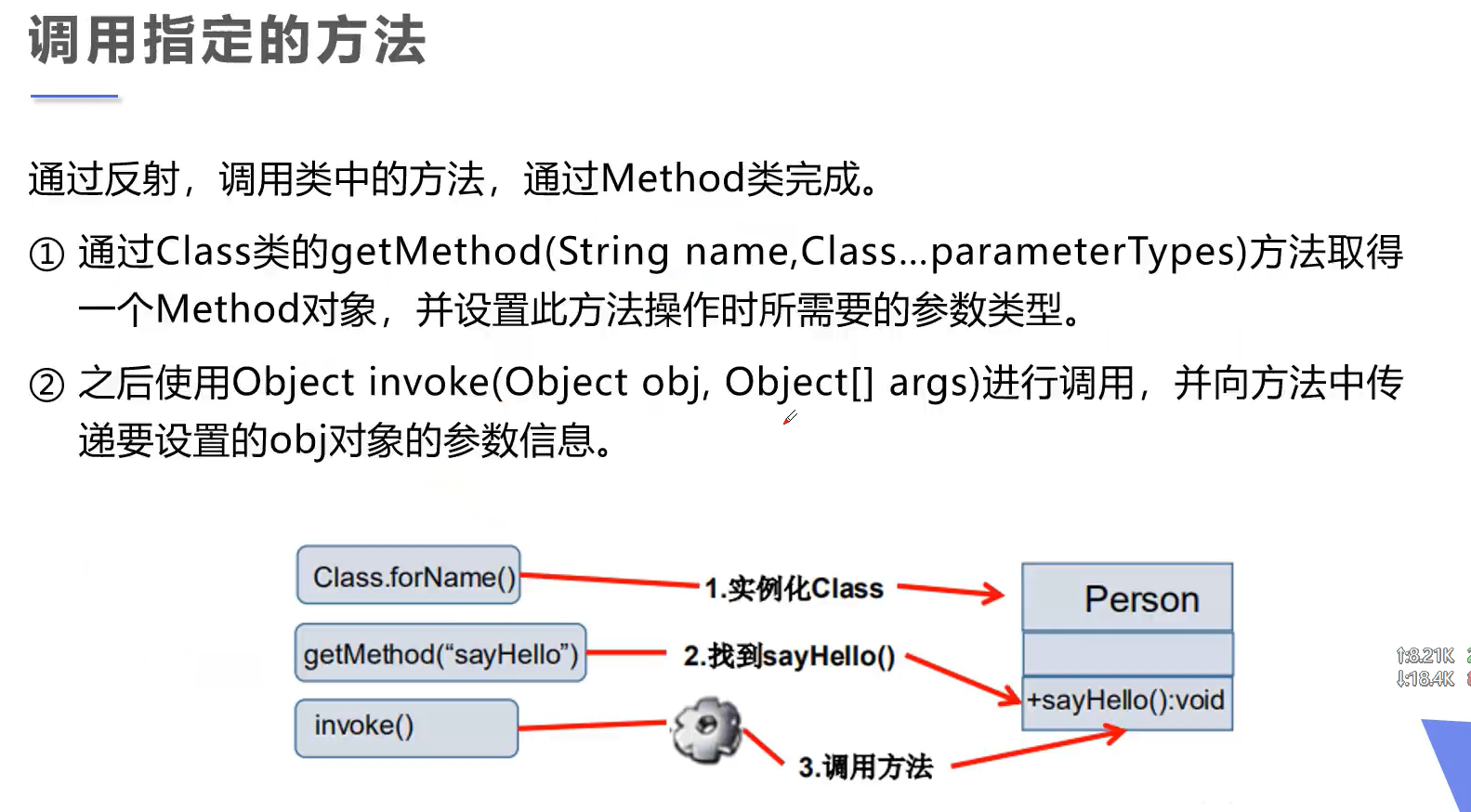


设置为true可提高效率, 当然远不及直接用正常的方法(new对象,对象调用)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| package com.zq.Reflect;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Use {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.zq.Reflect.user");
Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class);
user zq = (user) constructor.newInstance("zq", 18);
Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
setName.invoke(zq, "jamay");
System.out.println(zq);
Field id = c1.getDeclaredField("id");
id.setAccessible(true);
id.set(zq, 20);
System.out.println(zq);
}
}
|
效率测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| package com.zq.Reflect;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class EfficiencyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
test1();
test2();
test3();
}
public static void test1() {
user zq = new user("zq", 18);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
zq.getName();
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("正常方式10亿次用时" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
public static void test2() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
user zq = new user("zq", 18);
Class c1 = zq.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("getName");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
getName.invoke(zq, null);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("反射方式10亿次用时" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
public static void test3() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
user zq = new user("zq", 18);
Class c1 = zq.getClass();
Method getName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("getName");
getName.setAccessible(true);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000000; i++) {
getName.invoke(zq, null);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("反射方式关闭检测10亿次用时" + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
}
}
|
通过反射操作注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
| package com.zq.Reflect;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Table {
String value();
}
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@interface Column {
String name();
String type();
int length();
}
public class AnnotationAndReflect {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.zq.Reflect.Student");
Annotation[] annotations = c1.getAnnotations();
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
System.out.println(annotation);
}
Table annotation = (Table) c1.getAnnotation(Table.class);
System.out.println(annotation.value());
Field name = c1.getDeclaredField("name");
Column a = name.getAnnotation(Column.class);
System.out.println(a.name());
System.out.println(a.type());
System.out.println(a.length());
}
}
@Table("db_student")
class Student {
@Column(name = "Column_id", type = "int", length = 10)
private int id;
@Column(name = "Column_name", type = "String", length = 10)
private String name;
public Student() {
}
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|
















